Deliverability
What is DKIM: Learn how it works and why it’s necessary
You may know DKIM as an added layer of authentication for email but it’s more than that. It’s a digital signature that proves you are who you claim to be. DKIM also helps with your email deliverability. How? Keep reading and we’ll give you all the details.
PUBLISHED ON
Are you who you say you are, or are you a spoofer in disguise? Answering this question is what DKIM is all about.
As email usage and capabilities continue to grow, it’s important to make sure that your sender reputation is staying positive and secure. One of the best ways to do this is to use DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). If the idea of yet another email acronym is throwing you off, don’t be alarmed.
Below, we’ll walk through the basics and benefits of DKIM to illuminate its purpose and value to sender reputation.
Table of content
What is a DKIM signature?
What is a DKIM record?
What are DKIM record checks?
What are the benefits of DKIM?
Verify your domain
Add your records
Common DNS Provider Documentation
What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email authentication protocol that validates you as the true sender of a message using encrypted signatures. It ensures that nobody has used your domain or other identifiers to impersonate you or your company.
DKIM has become an authentication standard in the email world necessary for both bulk marketing and transactional campaigns. A message sent without DKIM and/or SPF can be considered suspicious by different email analysis tools.
How does DKIM work?
DKIM is a crucial component in safeguarding email security against phishing attacks. Employing domain-based message authentication, DKIM verifies the authenticity of emails by attaching a digital signature linked to the sending domain name. This signature acts as a stamp of legitimacy, ensuring that emails haven't been tampered with during transit and originate from authorized sources. By providing a mechanism to detect and prevent email spoofing, DKIM adds a layer of trust to online communications, crucial in an age where phishing attacks are rampant.
DKIM operates through a key pair system, where a private key is held by the email server and a corresponding public key is published in the DKIM signing domain's DNS records. To implement DKIM effectively, email servers need to be configured to sign outgoing emails with this private key.
This signing process embeds a cryptographic signature within the email header, serving as a digital fingerprint of authenticity. The DKIM signature is then verified by recipient servers against the public key stored in the DNS records of the sender's domain. This conformance ensures that emails are from the claimed sender and haven't been modified in transit. This also helps with email security. Matching keys open the door to deliverability. Mismatched keys trigger alarms and land you in spam.
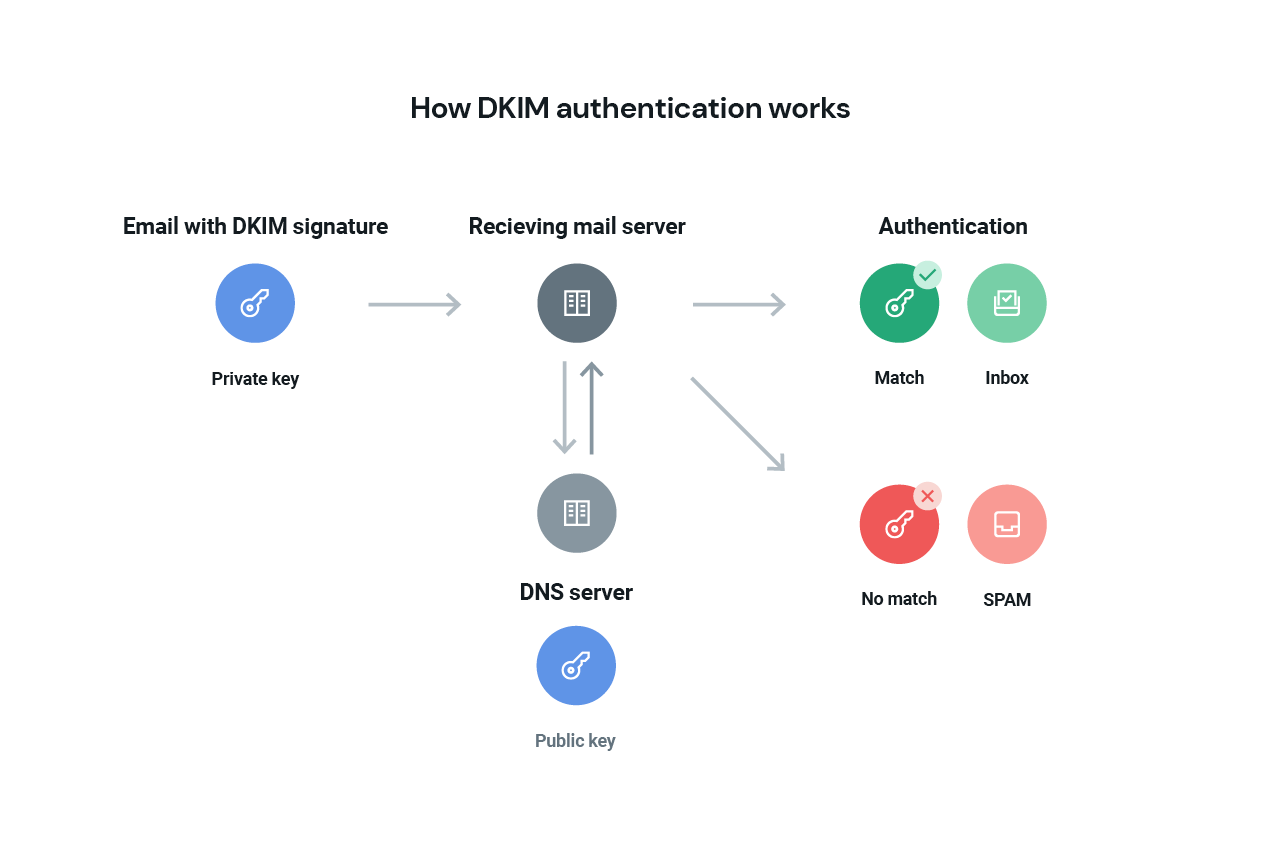
There are a few important elements in DKIM authentication, including DKIM signatures and DKIM records. Let’s see what they are and what role they play in this process.
What is a DKIM signature?
The main component of DKIM is the DKIM signature, a header that is attached to your email messages which your recipient can use for verification. How you generate DKIM keys varies depending on your provider but some basic recurring variables of the signature are:
“d=” refers to the signing domain associated with a selector record to locate a public key. Messages from Mailgun are identified as “d=mailgun.com”.
“b=” refers to the message’s unique DKIM signature of headers and body, encoded with Base64.
“bh” refers to a digital hash value that contains your encrypted private key (canonicalized by Base64) so it can be verified by the recipient.

Did you know? Base64 is used to safely carry data that has been encrypted, or stored, in a binary format over channels that usually only support text, like HTML and CSS.
Just like with adding your John Hancock to a document, your DKIM signature should be the last thing added to an out bounding message. Why? Modifications to an email’s content or its headers will alter its cryptographic hash (encoded information about the email content sent along with your encrypted key). Once sent, your DKIM signature – containing your encrypted private key– is validated by the recipient server.
How to keep your DKIM keys secure
Using public-key cryptography, fortifies email security by allowing email servers to sign messages with a private key and attach a signature header. To enhance security, it’s a good idea to use key rotation to periodically create new key pairs. Rotating keys mitigates the risk of compromised keys and ensures continued defense against potential attacks.
What is a DKIM record?
A DKIM record is part of your DNS records. Its purpose is to store the public domain key(s) – string of randomly generated characters – you use for DKIM. A simplified way of looking at it is to say that a DNS record is a listing of a domain and its IP address, and the DKIM record is a TXT record within the DNS record that contains a key used for email authentication.
If you don’t set up a DKIM record with your personal domain information, some email providers, like Google Mail, use their own default DKIM in your messages. However, it is always best to create your own specific DKIM records. Specific, endorsed records make verification and troubleshooting easier for both sender and recipient.
Need to set up multiple keys for your domain? Use a DKIM selector to set up multiple delivery services from a domain, or to send from a subdomain.
What are DKIM record checks?
A DKIM record check is pretty much what it sounds like – it means that you’re validating DKIM records to ensure they’re correct. DKIM record checks are particularly useful if you’re sending emails via SMTP. SMTP protocols don’t automatically include these layers of authentication, making them more vulnerable to spam and email-based hacks than sending via API.
DKIM record checks show the domain used to sign the DKIM signature, and validate that the email was authorized by the domain owner. Curious how to verify a record? Try it out with this handy DKIM checker tool.
Why is DKIM important?
DKIM provides protection for the reputation of your organization and the integrity of its email program. It offers domain protection against phishing and “spoofing” scams, especially when used with DMARC and SPF. DKIM is difficult to spoof since it detects inconsistencies in email headers and other unauthorized changes.
What are the benefits of DKIM?
Additionally, DKIM boosts your reputation. Because your messages can be verified, they are more likely to be trusted and recognized. Knowing that your emails are secure helps recipients feel more comfortable when they’re in contact with you. This can lead to more two-way communication between you and your email list, and help strengthen relationships with your customers.
DKIM helps ensure deliverability. Without a DKIM signature and valid records, recipients’ SMTP servers are significantly more likely to block your emails and mark them as spam . Remember we said that SMTP doesn’t have built-in layers of authentication? Well, if you provide it you’re that much more likely to land in the inbox.
How to set up DKIM with Mailgun
Mailgun requires a verified DKIM key via DNS check before a domain can send from its platform. Keep your messages as secure as possible by customizing your key. Instead of using a provider’s standard DKIM, you’re prompted to set up verification details that are specific to your domain and are associated with your organization. This keeps your emails easily identifiable by recipients—and it keeps your DKIM records recognizable and changeable for you and your team.
Below is a step-by-step guide on how to customize your DKIM with Mailgun.
Verify your domain
Add a domain you own and verify it by setting up the DNS record we provide (this is the DKIM record) at your DNS provider. An example is below.
1. Add your domain or subdomain in the Domains tab of the Mailgun control panel, or via the API.
2. Choose your DKIM key length. Longer keys equal more protection from spammers.
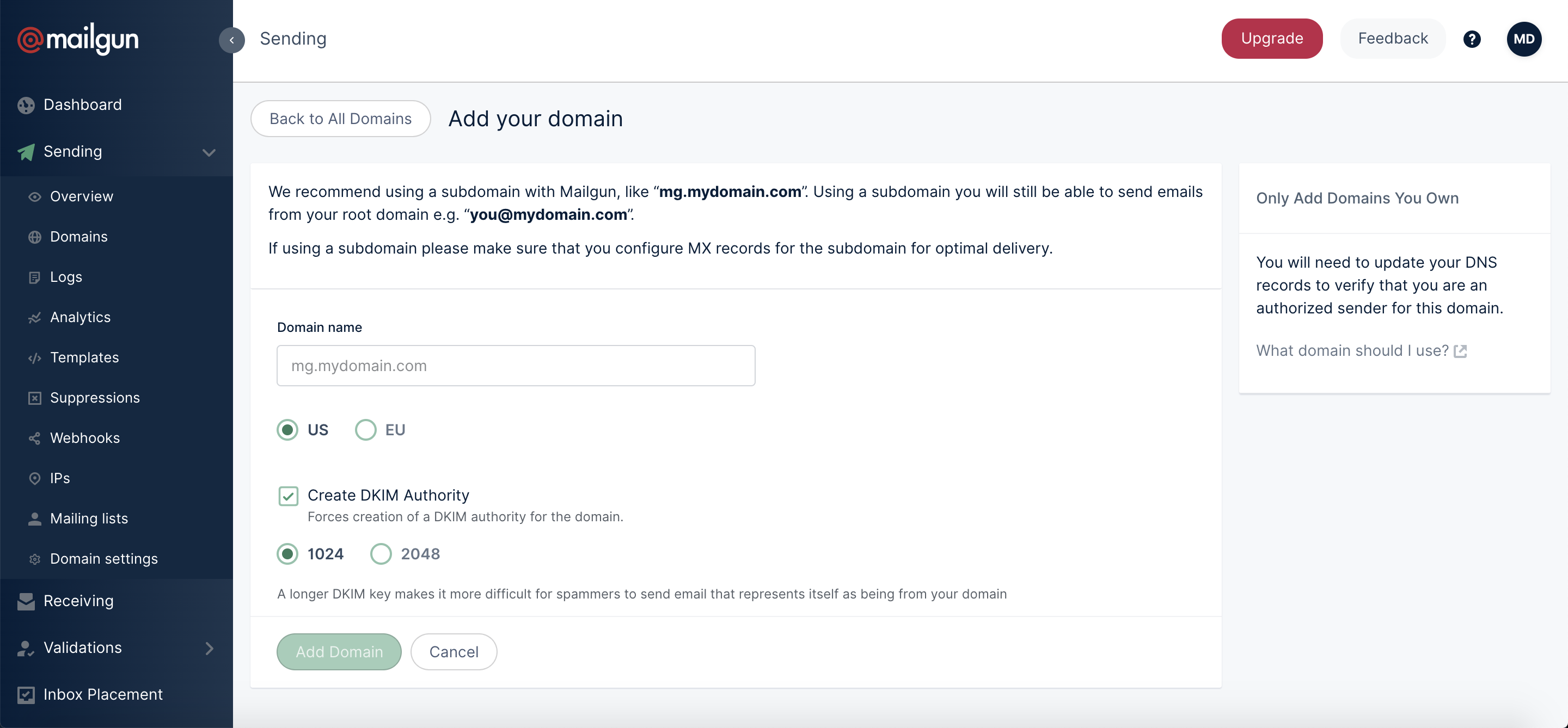
Add your records
3. Open your DNS provider and add the DKIM TXT DNS record provided. This record can be found in the Domain Verification & DNS section of the domain settings page of the Mailgun control panel.
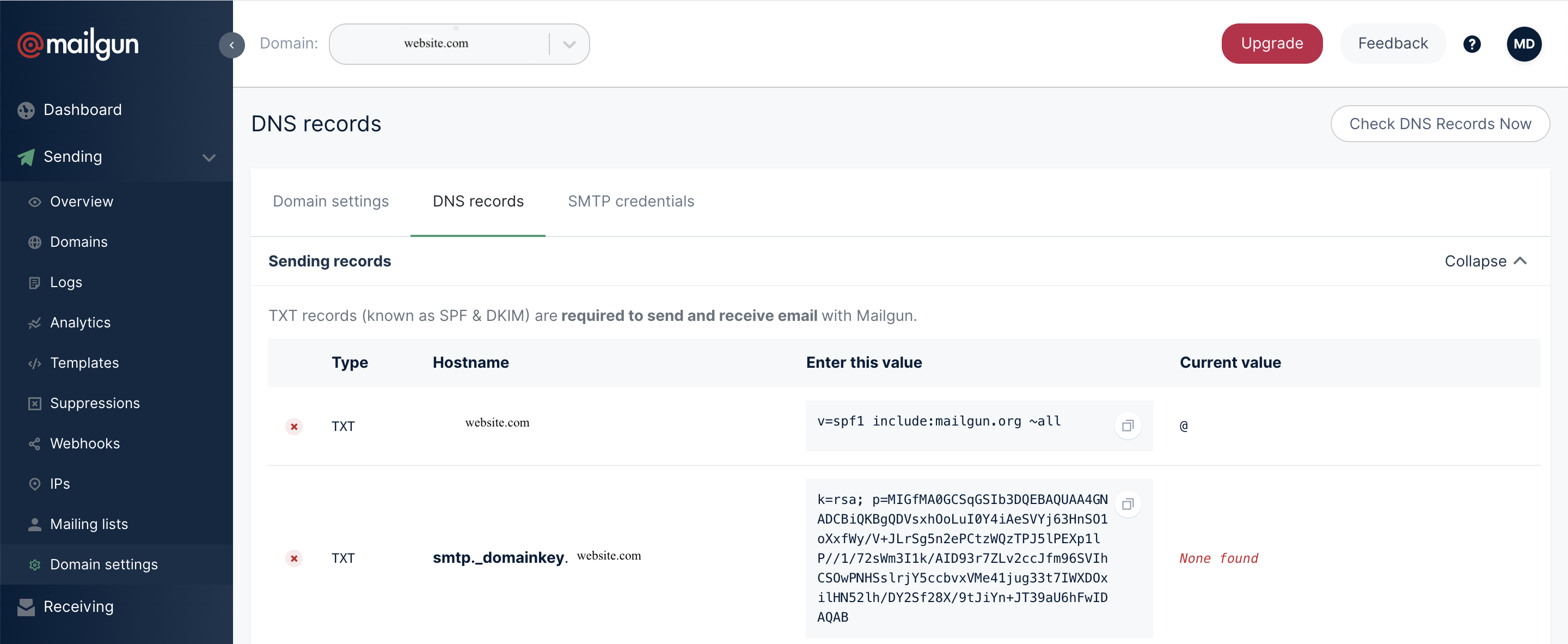
4. If you want Mailgun to track clicks and opens you can also add the CNAME record.
5. MX records should also be added, unless you already have MX records for your domain pointed at another email service provider (e.g., Gmail).
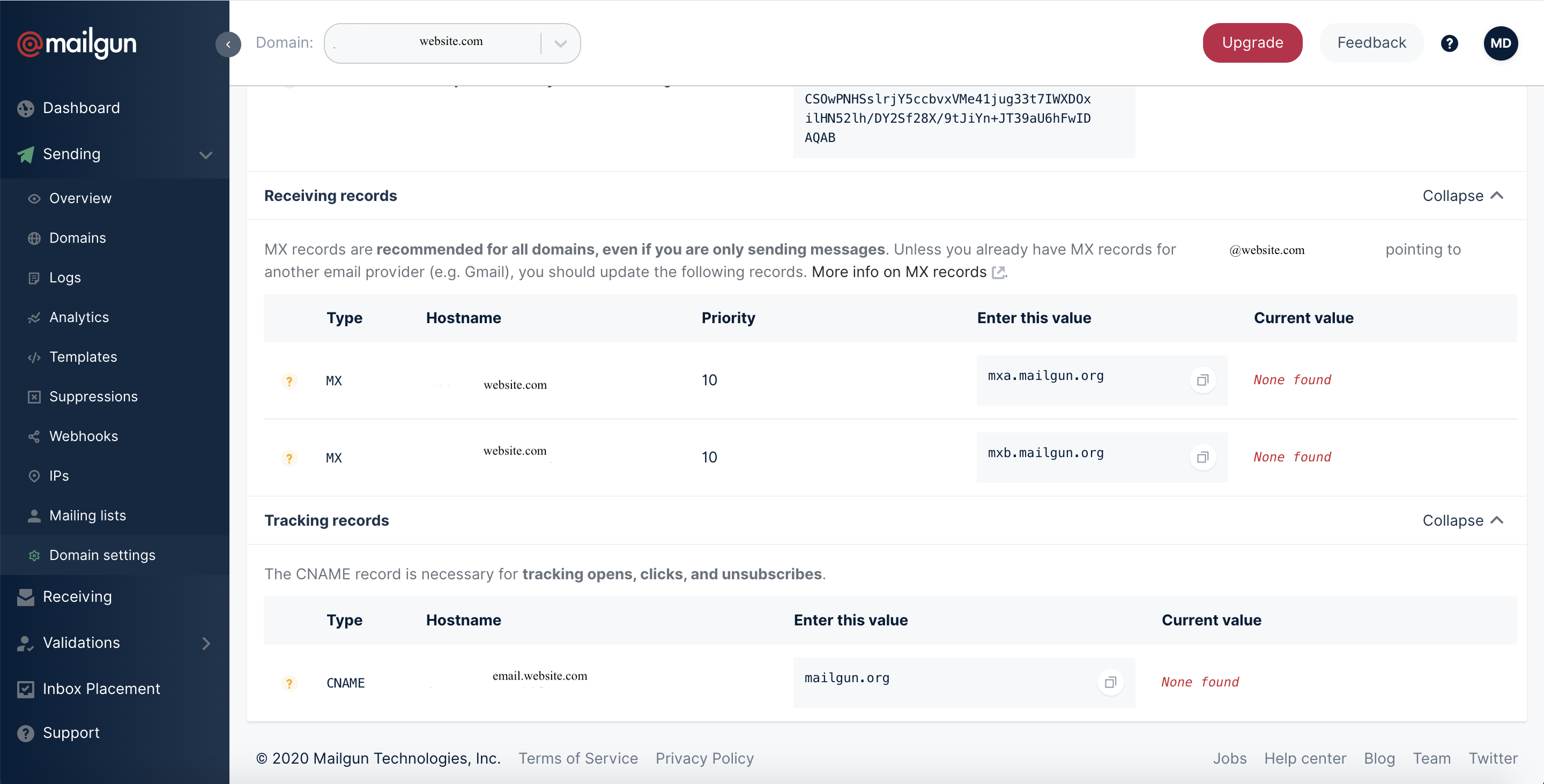
Once you’ve added the records and they’ve propagated, your domain will be verified. Note: it can take 24-48 hours for DNS changes to be verified.
Common DNS Provider Documentation
Common providers are listed below. If yours is not listed, contact your DNS provider for assistance:
NameCheap: All Records
Rackspace Email & Apps: All Records
Rackspace Cloud DNS: Developer Guide
Amazon Route 53: Developer Guide
Now you’re all set! If you get stuck, check out our documentation for more in-depth information on DKIM and step-by-step setup guides.
What you need to remember about DKIM and its usage
Why be vulnerable when you can be validated? DKIM is encrypted proof of your sender identity. It’s a useful tool that you can (and should) use to send email to your mailing list. By “signing” your emails, you signal that your organization is trustworthy.
DKIM offers your recipients protection from fraud, and boosts your sender reputation and deliverability rate by confirming your secure identify. It’s a small but crucial step – alongside other best practices, like cleaning and validating your email list – that strengthen your email program.
Need more help convincing mailbox providers you're really not a spammer in disguise? Learn more about email authentication, SPF, and DMARC, in our blog, and subscribe to our newsletter to stay in the loop.
Leveraging other email authentications
DKIM is definitely a standard industry authentication, but more mailbox providers are requiring senders to level up with DMARC.
While DKIM and SPF play crucial roles in email authentication, implementing DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) policies adds an extra layer of security against email fraud. DMARC builds upon DKIM and SPF by providing domain owners with visibility into how their domains are being used for email authentication. It allows domain owners to specify a DMARC policy, instructing ISPs (Internet Service Providers) and receiving mail servers on how to handle emails that fail authentication checks. Configuring DMARC policies can range from monitoring only to quarantine or reject actions, providing granular control over email delivery. By leveraging DMARC alongside DKIM and SPF, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of email spoofing and phishing attacks.